GitLab Runner
GitLab Runner is a service that runs jobs in CI/CD pipeline on your server. You can use shared runners from GitLab or install your own runner.
Documentation is available here: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner
Download
You have to install GitLab Runner on your server.
Note
You have to select the correct package for your OS and architecture. And you know to find your OS and architecture.
curl -LJO "https://gitlab-runner-downloads.s3.amazonaws.com/latest/deb/gitlab-runner_${arch}.deb"Find architecture
To find your architecture, you can use this command:
uname -aExample
Linux xxxxx 6.1.0-10-amd64 xxxxx x86_64 GNU/LinuxHere architecture is amd64.
Find distribution
lsb_release -aExample
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Debian
Description: Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm)
Release: 12
Codename: bookwormHere OS is Debian, so I will select deb packages. So, in this example, link is https://gitlab-runner-downloads.s3.amazonaws.com/latest/deb/gitlab-runner_amd64.deb
Installation
Install GitLab Runner
sudo dpkg -i gitlab-runner_${arch}.debINFO
To update GitLab Runner, download again the package and install it.
Install service
sudo gitlab-runner installConfiguration on GitLab
Now go to your GitLab instance and choose any project. Go to Settings > CI/CD and expand Runners section.
INFO
Your runner will be available for all projects in your GitLab instance.
Select New project runner
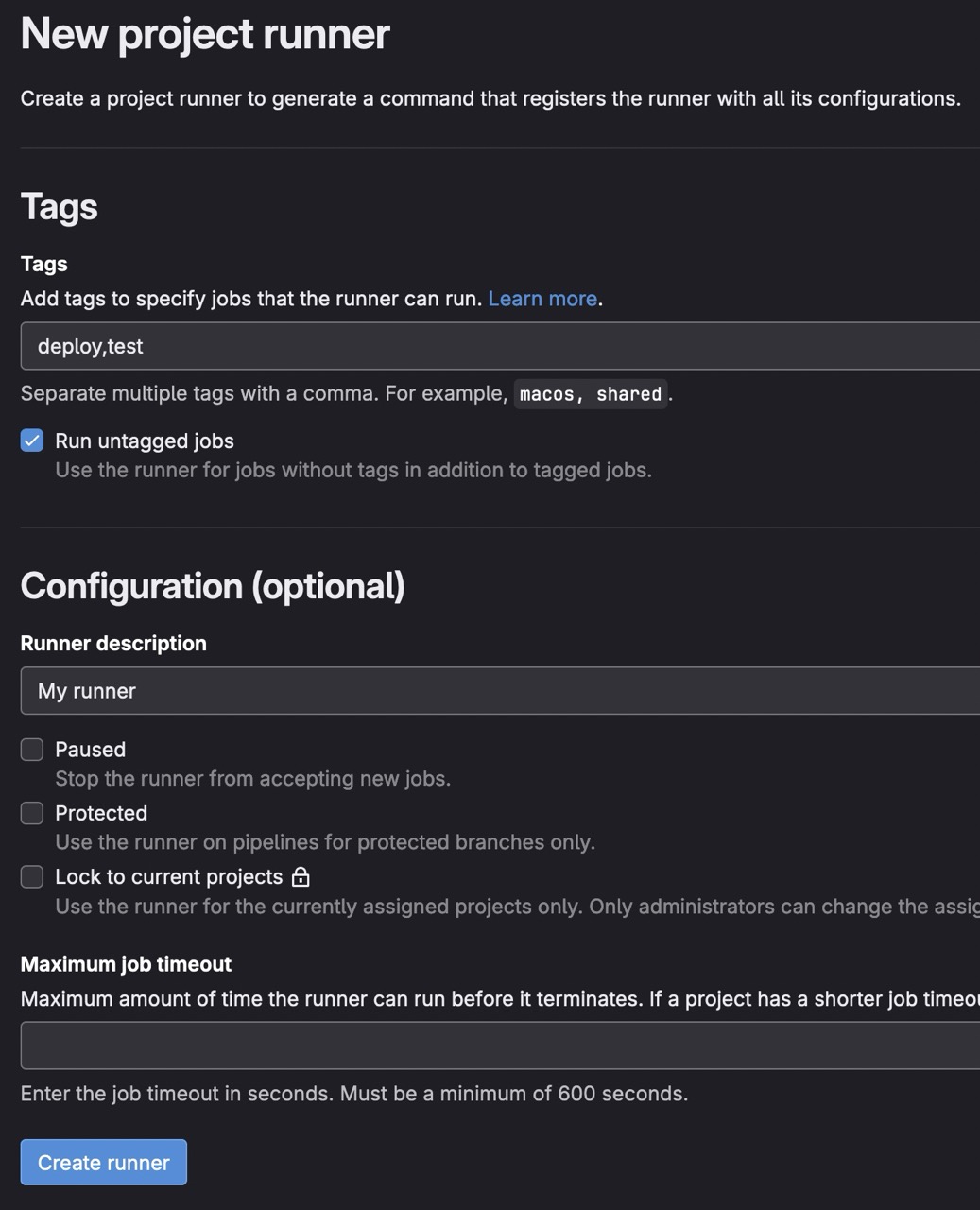
You will a new screen to config your runner.
INFO
I advice to check Run untagged jobs and pay attention to Tags field. You have to set tags used in your .gitlab-ci.yml file. In my example, my configs use often deploy and test tags. If a job has deploy tag, it will be executed by this runner, BUT if a job is tagged with docker tag, this runner will not execute it.
# Tag used here is `deploy`, so this job will be executed by runner with `deploy` tag
stages:
- deploy # This is a stage
deploy-job:
stage: deploy # This is a jobWhen you finish, click on Create runner.
On new screen, keep Linux for the Operating systems and pay attention to the token. In this example, it's glrt-s6u2ZR1xJNsMW4yUDhrR, keep it for the next step.
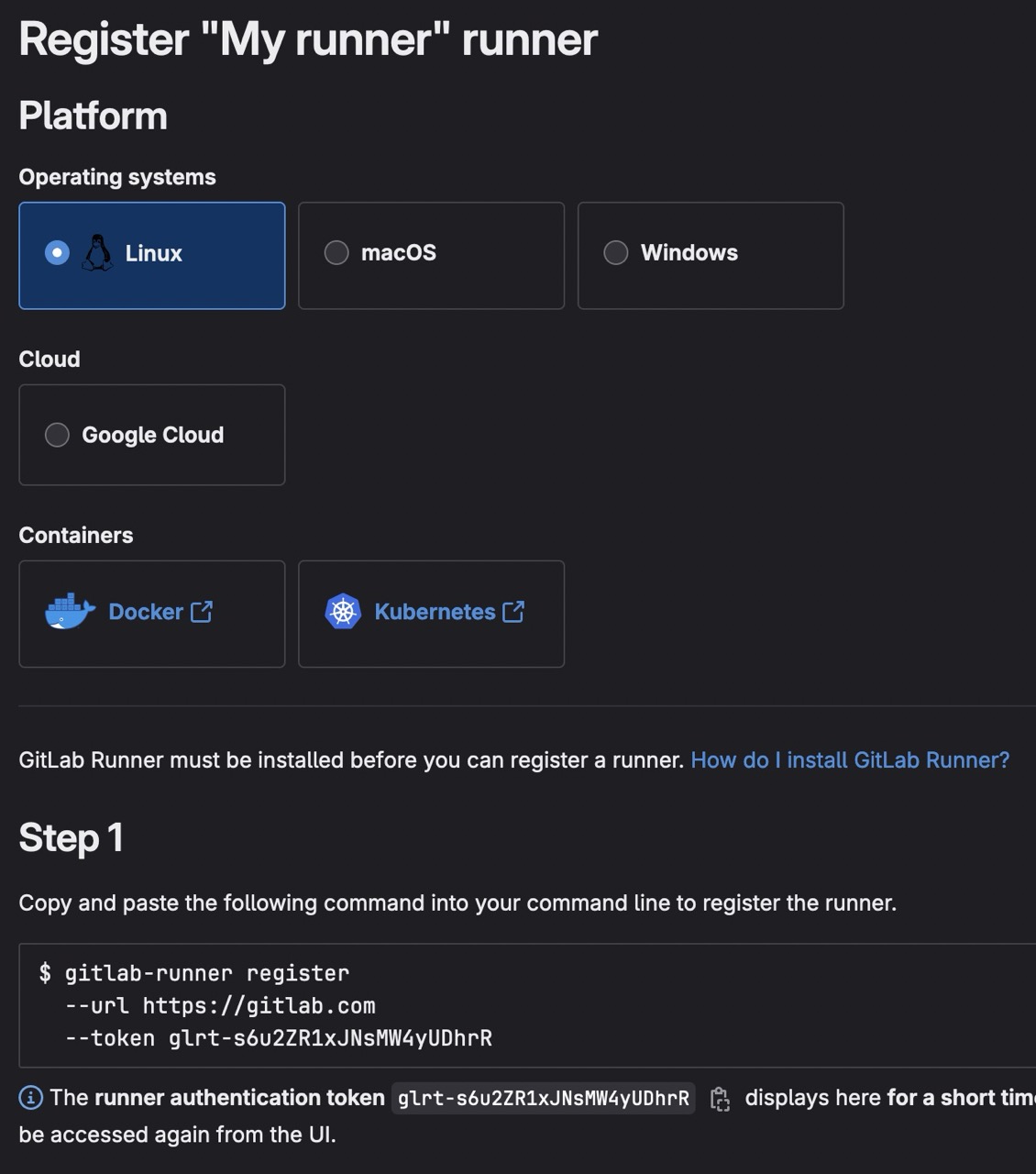
Configuration on server
Now, you have to register your runner on your server.
sudo gitlab-runner registerEnter the GitLab instance URL (for example, https://gitlab.com/):I choose https://gitlab.com/ because I use GitLab SaaS. If you use your own GitLab instance, you have to enter your URL.
Enter the registration token:Enter the token you got from the previous step.
Enter a name for the runner. This is stored only in the local config.toml file:You can enter any name you want. I keep default name, it's hostname.
Enter an executor: ssh, docker, docker-autoscaler, custom, shell, docker-windows, docker+machine, kubernetes, instance, parallels, virtualbox:I choose docker because I want to execute my jobs in Docker containers.
Enter the default Docker image (for example, ruby:2.7):If you choose docker executor, you have to enter a default Docker image. I choose alpine:latest.
Runner registered successfully. Feel free to start it, but if it's running already the config should be automatically reloaded!
Configuration (with the authentication token) was saved in "/path/to/.gitlab-runner/config.toml"Now, your runner is registered and you can start it.
sudo gitlab-runner startYou can check the status of your runner.
sudo gitlab-runner statusStart GitLab Runner
sudo gitlab-runner start my-runnerEnable Runner for project
Now, you have to enable your runner for your project.
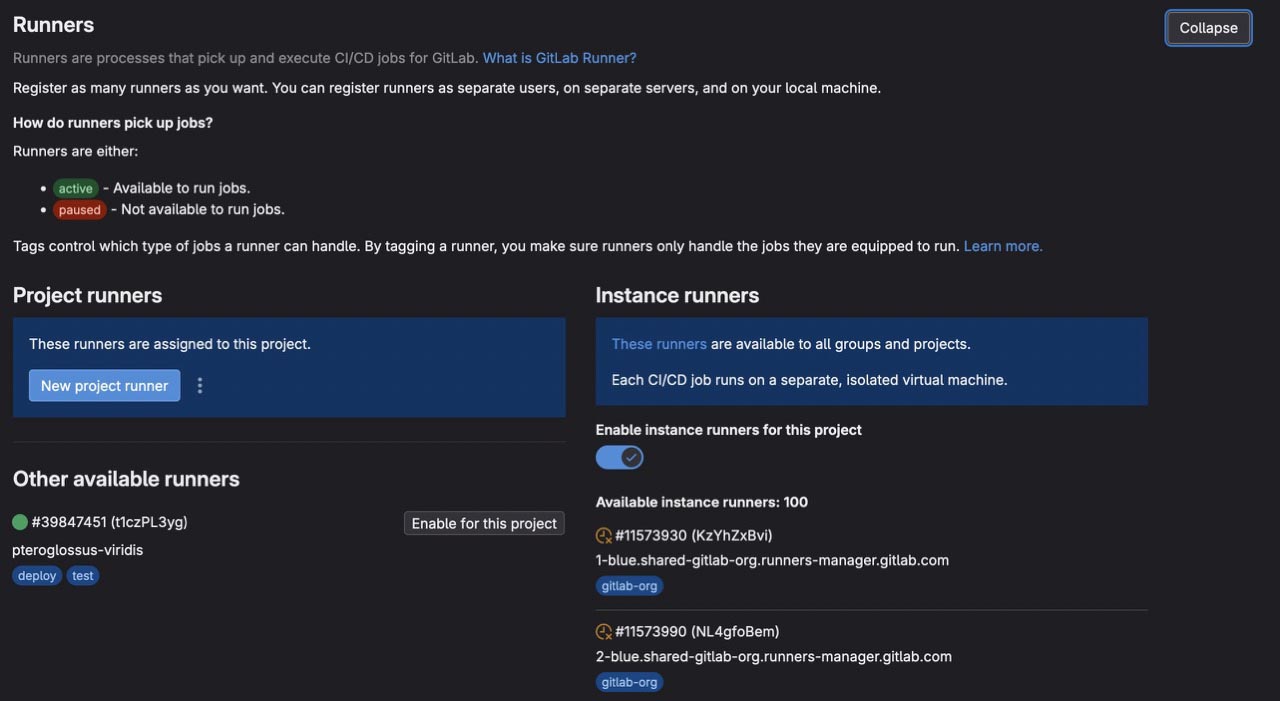
Go to your project in GitLab, and go to Settings > CI/CD > Runners.
You will see your runner in the Project runners list, click on Enable for this project.
INFO
You can disable GitLab shared runners, to use only your runners. See right panel with Instance runners and uncheck Enable instance runners for this project.
Commands
Start
sudo gitlab-runner startStatus
sudo gitlab-runner statusStop
sudo gitlab-runner stopUnregister
sudo gitlab-runner unregister --all-runnersTips
Deploy from GitLab CI/CD
To deploy your project from GitLab CI/CD, you have to add your SSH key to your GitLab project.
- In
before_scriptstep, you have to add your SSH key to the runner - In
scriptstep, you can deploy your project
INFO
To know more about GitLab CI/CD variables, check this guide.
We take an example with this base .gitlab-ci.yml file:
stages:
- deploy
deploy-job:
stage: deploy
image: node:20.16.0
before_script:
script:
only:
- mainSSH key
In this part, you have to add your SSH key to your GitLab project. You have to add three variables:
SSH_PRIVATE_KEY: Your SSH private key,SSH_PORT: Your SSH port, like22SSH_IP: Your SSH IP, like123.456.789.0
TIP
To avoid to repeat your variables, you can add them as group variables, to know more about group variables, check this guide.
before_script:
- "command -v ssh-agent >/dev/null || ( apk add --update openssh )"
- eval $(ssh-agent -s)
- echo "$SSH_PRIVATE_KEY" | tr -d '\r' | ssh-add -
- mkdir -p ~/.ssh
- chmod 700 ~/.ssh
- ssh-keyscan -p $SSH_PORT $SSH_IP >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts
- chmod 644 ~/.ssh/known_hosts
- apt-get update -qq && apt-get install -y -qq sshpass
- apt-get install -y -qq rsyncNow, your SSH key is added to your runner, and your runner can clone your project, private or public.
INFO
In this example, I add rsync to my runner to deploy my project.
Build
In this part, you have to build your project. In this example, we use a Memorandum, a Vitepress project.
In these steps, we clone the project, install dependencies and build the project.
before_script:
- echo "Checkout..."
- git clone https://gitlab.com/kiwilan/memorandum.git
- cd memorandum
- npm install -g pnpm
- pnpm i
- echo "Building..."
- pnpm buildDeploy
In this part, you have to deploy your project.
- We use
rsyncto copy thedistfolder to our server. - We use
sshto connect to our server and pull the project.
Why don't build on the server?
You can build your project directly on your server, but it will take some seconds and during this time, your site will be down. With current method, your site will receive the new version only when the build is finished.
script:
- rsync -azPhhr -e "ssh -p $SSH_PORT" .vitepress/dist $SSH_USER@$SSH_IP:/home/$SSH_USER/www/$CI_PROJECT_NAME/.vitepress/dist-$CI_JOB_ID
- ssh -p $SSH_PORT $SSH_USER@$SSH_IP "
. ~/.zshrc &&
cd /var/www/$CI_PROJECT_NAME &&
git pullINFO
The $CI_JOB_ID variable is available in GitLab CI/CD. You can find a list of predefined variables here: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/variables/.
Complete .gitlab-ci.yml
stages:
- deploy
deploy-job:
stage: deploy
image: node:20.16.0
before_script:
- "command -v ssh-agent >/dev/null || ( apk add --update openssh )"
- eval $(ssh-agent -s)
- echo "$SSH_PRIVATE_KEY" | tr -d '\r' | ssh-add -
- mkdir -p ~/.ssh
- chmod 700 ~/.ssh
- ssh-keyscan -p $SSH_PORT $SSH_IP >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts
- chmod 644 ~/.ssh/known_hosts
- echo "Installing dependencies..."
- apt-get update -qq && apt-get install -y -qq sshpass
- apt-get install -y -qq rsync
- echo "Checkout..."
- git clone https://gitlab.com/kiwilan/memorandum.git
- cd memorandum
- npm install -g pnpm
- pnpm i
- echo "Building..."
- pnpm build
script:
- rsync -azPhhr -e "ssh -p $SSH_PORT" .vitepress/dist $SSH_USER@$SSH_IP:/home/$SSH_USER/www/$CI_PROJECT_NAME/.vitepress/dist-$CI_JOB_ID
- ssh -p $SSH_PORT $SSH_USER@$SSH_IP "
. ~/.zshrc &&
cd /var/www/$CI_PROJECT_NAME &&
git pull &&
docker exec $DOCKER_CONTAINER rm -rf /usr/share/nginx/html/node_modules &&
docker exec $DOCKER_CONTAINER rm -rf /usr/share/nginx/html/.vitepress/dist &&
docker cp .vitepress/dist-$CI_JOB_ID/dist $DOCKER_CONTAINER:/usr/share/nginx/html/.vitepress/dist &&
docker restart $DOCKER_CONTAINER &&
rm -rf .vitepress/dist-$CI_JOB_ID &&
docker logs $DOCKER_CONTAINER
only:
- main